A function is a self-contained
block of program statements that performs a particular task. The concept of C programming
is combination of functions and the program execution will begins from the
special function called main(). The scanf(), printf() main() etc.. that have
been used in programs so far are all functions. They are called library
functions and C provides a lot of them.In addition to built in library
functions, the programmers can write their own functions and use them.These are called user defined functions.
When there are multiple functions
in a program , each function is given different name and a list of parameters. When
ever the function is to be called, we refer the function name with suitable
list of arguments. The program control will then be transferred to the function
and the statements in the function will be executed. After the called function
is executed, the control returns to the calling function, the place it was
called from.A function can call another function, and that another and so on.
Why Functions
The use of functions provides
several benefits.
It makes programs significantly
easier to understand and maintain by breaking them up into easily manageable
chunks.
Code reuse/Code sharing is the
another advantage, where the same code can be used where ever needed. This will
avoid the need to have same code replicated at various points and hence make
the program small and efficient. A well written function may be reused in
multiple programs. C standard library is an example of functions being reused.
Flexible debugging is another
advantage because functions make the code shorter and more readable.
Data protection is another
feature of functions. The local data described within the functions are not available
outside and are used only when they are executed.
Functions form an important part of
top-down design and structured programming. Top down design is the act of
breaking down a task into manageable parts such that each individual part is
relatively simple and the parts can be combined without much difficulty to
achieve the original task. Structured programming makes the code more elegant
and readable.
Using Functions
The following 3 components are
associated with the use of functions
1.The declaration statement (
function prototype declaration) that identifies a function with a name, list of
arguments and the type of data returned.
Syntax:
return_data_type
function_name(data_type var1,data_type var2,…….);
Eg: int max(int a,int b); // this function max will return the maximum
of 2 integers a and b.a and b are called the arguments of the function.
float average(int n,float a[]); // function average to find average
of elements of the array a of size n
Note: if the function does not return any value void has to be
mentioned. The default return value of a function is int. Function declaration
is needed if the called function is written later. The function name should not
match with built in function names.
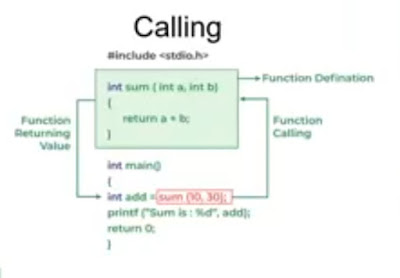
2.The function definition that
consists of a function header identifying the function, followed by the body of
the function, which contain the statements to be executed.
Eg:
int sum(int a, int b)
{
return a+b;
}
Note: The sum function sum return the sum of a and b.The job of return statement is to hand over some value from the
function to the point where the call was made.
3.The calling statement that invokes the function by either passing or
not passing some parameters.
add=sum(10,30);
int x=10,y=30;
add=sum(x,y); // x and y are called actual parameters, whereas a and b in definition is called formal parameters.
This sum function will add 10 and 30 and return the sum , which is stored in to the variable add.
Note:
The name, number of arguments and type must match
with the function definition.
The parameters/variables used and its type as they appear in the prototype of the function or method is called formal parameters. Eg: a and b in the sum function definition
The variable or expression corresponding to a formal parameter that appears in the function or method call in the calling environment is called actual parameters. Eg x and y used to call the add function.
Arguments are passed by value in normal C function calls.
This means that the local copies of the values of the arguments are passed.
Factorial of a number using a function and computing nCr using the function
#include <stdio.h>
long long int fact(int n)
{
int i,f=1;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++) f=f*i;
return(f);
}
int main()
{ int n,r,ncr;
printf("Enter the value of n\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter the value of r\n");
scanf("%d",&r);
ncr=fact(n)/(fact(r)*fact(n-r));
printf("%dC%d=%d",n,r,ncr);
return 0;
}
Sample program to find power
x^k using a function
#include <stdio.h>
int power(int x, int k)
{
int r=1,i;
for (i=1;i<=k;i++)
r=r*x
return r;
}
int main()
{
Int x,k,p;
printf(“Enter x and k \n”);
scanf(“%d%d”,&x,&k);
p=power(x,k);
printf(“%d power %d= %d”,x,k,p);
}
Note: The variables used in calling the function are called actual
arguments and the variables used in function header are called formal
arguments.
Binary to decimal conversion using function(university question)
Binary to decimal conversion using function(university question)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int convert(long long n)
{
int dec = 0, i = 0, rem;
while (n != 0) {
rem = n % 10;
n /= 10;
dec += rem * pow(2, i);
++i;
}
return dec;
}
int main()
{
long long n;
printf("Enter a binary number: ");
scanf("%lld", &n);
printf("%lld in binary = %d in decimal\n", n, convert(n));
return 0;
}
#include <math.h>
int convert(long long n)
{
int dec = 0, i = 0, rem;
while (n != 0) {
rem = n % 10;
n /= 10;
dec += rem * pow(2, i);
++i;
}
return dec;
}
int main()
{
long long n;
printf("Enter a binary number: ");
scanf("%lld", &n);
printf("%lld in binary = %d in decimal\n", n, convert(n));
return 0;
}
Passing Array as arguments to a function
When an entire array is an argument of a function, only the address of the array is passed and not the copy of the complete array. Therefore, when the function is called with the name of the array as argument, address to the first element is handed over to the function. This implies that during its execution, the function has the ability to modify the contents of the array that is specified as function argument. This is an exception to the rule of passing the function arguments by value.Arrays are passed by reference.
Example:
The following function modify(a[],i,x) will modify the i th element of the array with a value x.Note that the array element is modified in the main.
#include <stdio.h>
modify(int a[10],int i,int x)
{
a[i]=x;
}
int main()
{
int a[10]={10,20,12,11,34,25,67,30,50,70};
int i;
modify(a,6,100);
for(i=0;i<10;i++) printf("%d\t",a[i]);
}
output:
10 20 12 11 34 25 100 30 50 70
Write a C program to find the largest and smallest element in an integer array using function. ( university question )
#include <stdio.h>
void arraysl(int a[],int n)
{
int l,s,i;
l=a[0];
s=a[0];
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
if(a[i]>l) l=a[i];
if(a[i]<s) s=a[i];
}
printf("Smallest=%d largest=%d \n",s,l);
}
int main()
{
int a[100],n,i;
printf("Enter the number of elements..:");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter the array elements....\n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
arraysl(a,n);
}
#include <stdio.h>
void arraysl(int a[],int n)
{
int l,s,i;
l=a[0];
s=a[0];
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
if(a[i]>l) l=a[i];
if(a[i]<s) s=a[i];
}
printf("Smallest=%d largest=%d \n",s,l);
}
int main()
{
int a[100],n,i;
printf("Enter the number of elements..:");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter the array elements....\n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
arraysl(a,n);
}
Write a C program to find sum and average of an array of integers using user defined functions.(university question)
#include <stdio.h>sum_average(int a[10],int n)
{
int i;
float sum,avg;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
sum=sum+a[i];
avg=sum/n;
printf("Sum=%f Average =%f\n",sum,avg);
}
int main()
{
int a[10]={10,20,12,11,34,25,67,30,50,70};
int i;
sum_average(a,10);
}
Write a function in C which takes a 2-Dimensional array storing a matrix of numbers and the order of the matrix (number of rows and columns) as arguments and displays the sum of the elements stored in each row. ( university question)
#include <stdio.h>
void sumrow(int a[5][5],int m,int n)
{
int i,j,sum;
printf("Sum of the elements in each row\n");
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{sum=0;
for(j=0;j<5;j++)
sum=sum+a[i][j];
printf("Sum of elements in row %d=%d\n",i,sum);
}
}
int main()
{
int a[5][5]={{1,2,3,4,5},{2,3,1,1,1},{2,2,2,2,2},{1,1,1,1,1},{2,3,4,1,1}};
sumrow(a,5,5);
}
Functions help to modularize the program using functions and hence reduce the code
Matrix multiplication program using functions
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void readmatrix(int X[50][50],int m,int n)
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<m;i++)
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
scanf("%d",&X[i][j]);
}
void printmatrix(int X[50][50],int m,int n)
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<m;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
printf("%5d",X[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
void multiplymatrix(int A[50][50],int m,int n,int B[50][50],int p,int q,int C[50][50])
{ int i,j,k;
for(i=0;i<m;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<q;j++)
{ C[i][j]=0;
for(k=0;k<n;k++)
C[i][j]=C[i][j]+A[i][k]*B[k][j];
}
}
}
int main()
{
int A[50][50],B[50][50],C[50][50],m,n,p,q,i,j,k;
printf("Enter the dimensions of matrix A \n");
scanf("%d%d",&m,&n);
printf("Enter the dimensions of matrix A \n");
scanf("%d%d",&p,&q);
if ( n!=p ) { printf("Cannot multiply\n"); exit(0);}
printf("Enter matrix A\n");
readmatrix(A,m,n);
printf("Enter matrix B\n");
readmatrix(B,p,q);
multiplymatrix(A,m,n,B,p,q,C);
printf("The product matrix C\n");
printmatrix(C,m,q);
return 0;
}
Writing your functions for string handling
int mystrlen(char str[100])
{
int i;
for (i=0;str[i]!='\0';i++);
return(i);
}
void mystrcpy(char s2[100],char s1[100])// copy from s1 to s2
{
int i;
for(i=0;s1[i]!='\0';i++)
s2[i]=s1[i];
s2[i]='\0';
}
void mystrrev(char str[100])
{
int i,j;
char rstr[100];
for(i=0;str[i]!='\0';i++);
i--;
for(j=0;i>=0;i--,j++) rstr[j]=str[i];
rstr[j]='\0';
mystrcpy(str,rstr);
}
{
int i;
for (i=0;str[i]!='\0';i++);
return(i);
}
void mystrcpy(char s2[100],char s1[100])// copy from s1 to s2
{
int i;
for(i=0;s1[i]!='\0';i++)
s2[i]=s1[i];
s2[i]='\0';
}
void mystrrev(char str[100])
{
int i,j;
char rstr[100];
for(i=0;str[i]!='\0';i++);
i--;
for(j=0;i>=0;i--,j++) rstr[j]=str[i];
rstr[j]='\0';
mystrcpy(str,rstr);
}
// with out using a temporary array
void mystrrev(char str[100])
{
int i,j;
char t;
for(i=0;str[i]!='\0';i++);
i--;
for(j=0;j<i;i--,j++)
{t=str[i];
str[i]=str[j];
str[j]=t;
}
}
void mystrcat(char s1[100],char s2[100]) // concatenate s2 to s1
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;s1[i]!='\0';i++);
for(j=0;s2[j]!='\0';j++,i++)
s1[i]=s2[j];
s1[i]='\0';
}
void mystrupper(char str[100])
{
int i;
for(i=0;str[i]!='\0';i++)
if(str[i]>='a' && str[i]<='z') str[i]=str[i]-32;
}
{
int i,j;
char t;
for(i=0;str[i]!='\0';i++);
i--;
for(j=0;j<i;i--,j++)
{t=str[i];
str[i]=str[j];
str[j]=t;
}
}
void mystrcat(char s1[100],char s2[100]) // concatenate s2 to s1
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;s1[i]!='\0';i++);
for(j=0;s2[j]!='\0';j++,i++)
s1[i]=s2[j];
s1[i]='\0';
}
void mystrupper(char str[100])
{
int i;
for(i=0;str[i]!='\0';i++)
if(str[i]>='a' && str[i]<='z') str[i]=str[i]-32;
}
Try the following programs using functions
1.Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius.
2.Binary to decimal using function.
3.Finding x^k , use x and k as arguments.
4.Function to reverse a number.
5. Çheck whether a given year is leap year or not.( return 0 or 1)
6.Write a function big() to find the biggest of two numbers and use it
to find biggest of three numbers.
7.Write a function IsPrime(n) which will return 1 if the number is prime else it will return 0.
8.Sort array of integers( bubble sort-use array and n as arguments)
9.Add a string to the end of another string with out using library
function.(concatenation-uq)
10.Copy one string to another with out using library function.(uq)
11.Write a function to reverse a string and use it to check whether
the given string is palindrome or not.
12.Modify a char in a particular position of a string. Use position
and char as argument.
13.Find maximum value in an array.( use array as arguments)
14.Write a function in C which takes a 2-Dimensional array storing a matrix of numbers and
the order of the matrix (number of rows and columns) as arguments and displays the sum
of the elements stored in each row.(uq)
15.Write matrix addition of 3 matrices A,B and C. write functions for
reading and printing matrices.
16.Write functions to convert feet to inches and inches to centimeters.
Write a program which will read feet and convert it into centimeters using the
two functions.(uq)
17.Factorial of a given number.
18.Use the factorial function to compute nCr.
19.Use the factorial and power function to compute the series
1-x^2/2!+x^4/4!-x^6/6!...n.
20.Write a function to find the decimal equivalent of a binary number.(uq)
20.Write a function to find the decimal equivalent of a binary number.(uq)
21.Write a function in C which takes a 2-Dimensional array storing a matrix of numbers and the order of the matrix (number of rows and columns) as arguments and displays the sum of the elements stored in each row. ( uq).
22.Write an easy to read C program to find the value of a mathematical function
f which is defined as follows. f(n) = n! / (sum of factors of n), if n is not prime and f(n) = n! / (sum of digits of n), if n is prime.
f which is defined as follows. f(n) = n! / (sum of factors of n), if n is not prime and f(n) = n! / (sum of digits of n), if n is prime.
23.Write a C program to find sum and average of an array of integers using user defined functions.(uq)
24.Generate the series 2,5,12,20,30...etc ( Hint : nth term is n^2 +n ). Write a function which will return the n th term of this series and use this to generate the series.
25.Write a function which will take a string and a character as arguments and return the number of occurrence of the character in the string.




Comments
Post a Comment